Donor For Liver Transplant
Donor
Living Donor Liver Transplant
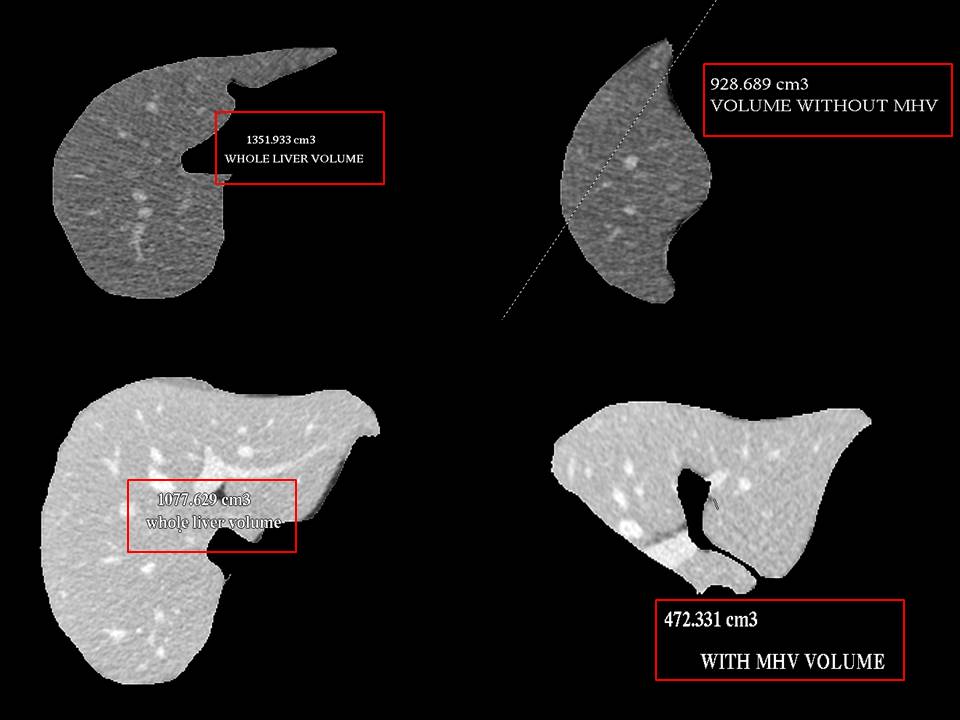
Like Japan and Korea, majority of liver transplants in India have been from living donors from the patient's family. Such a liver donor is a family member of the patient who volunteers to have an operation to have a portion of his/ her liver removed for transplantation into the patient. Liver has a large reserve of function and a remarkable ability to recover from injury. This means that up to 70% of normal healthy liver can be removed safely and the remaining liver will function and grow to the size of a normal liver. 90% of this growth happens in 2-3 months although slow growth occurs after that as well. The liver function tests (LFT) typically return to normal in 5-7 days. Ideally, the donor must be between the ages of 18 and 60, have a blood group compatible with that of the patient and be healthy and fit for surgery. Overweight people and those who consume alcohol regularly are usually not suitable.
The amount of liver removed from the donor depends on the weight of the patient and the size and anatomy of the liver. As a general rule, the weight of liver required for transplant is 0.8% of the weight of the patient. This means a 70 kg patient requires at least 560 g of liver to be transplanted.
Like anyone undergoing abdominal surgery, the donor should avoid lifting heavy weights for 3 months. After that there is no restriction on activity.
Deceased (Cadaveric) Donor Liver Transplant
Deceased (Cadaveric) donor is a person who is declared ‘brain-dead’ but who can donate other organs of his body as the blood supply to these organs is maintained. The organs of such a ‘brain-dead’ person can be used for transplantation if the next-of-kin give consent. Donor should be blood group compatible. Unfortunately, due to various socio-cultural factors, this form of organ donation is rare in India and the chances of getting such an organ in time are poor for a sick patient.
